Quadtree encoding (a simple compression algorithm)
April 10, 2010
The quadtree encoding allows us to describe a 2N×2N black and white image as a sequence of bits (0 and 1). Those sequences are to be read from left to right like this:
- the first bit deals with the complete 2N×2N region;
- "0" denotes a split: the current 2n×2n region is divided into 4 sub-regions of dimension 2n-1×2n-1, the next bits contains the description of the top left, top right, bottom left and bottom right sub-regions - in that order;
- "10" indicates that the current region contains only black pixels;
- "11" indicates that the current region contains only white pixels.
Consider the following 4×4 image (colored marks denote places where a split can occur):
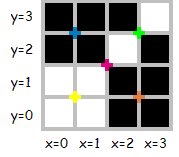
This image can be described by several sequences, for example : "001010101001011111011010101010", of length 30, or "0100101111101110", of length 16, which is the minimal sequence for this image.
For a positive integer N, define DN as the 2N×2N image with the following coloring scheme:
- the pixel with coordinates x = 0, y = 0 corresponds to the bottom left pixel,
- if (x - 2N-1)2 + (y - 2N-1)2 ≤ 22N-2 then the pixel is black,
- otherwise the pixel is white.
What is the length of the minimal sequence describing D24 ?
Written by gamwe6 who lives and works in San Francisco building useful things. You should follow him on Twitter